Shockwave tendonitis relief involves understanding its micro-tear and inflammation cause. Rest, physical therapy, and non-invasive methods like Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT) are key treatments. ESWT offers lasting pain reduction and improved function compared to corticosteroids, with evidence showing it modulates inflammation, enhances collagen synthesis, and improves tendon integrity for whiplash or sports injury recovery.
“Discover the science behind shockwave therapy as a potential solution for pain relief in cases of shockwave tendonitis. This condition, characterized by inflammation of tendons due to repetitive stress, often leaves sufferers seeking effective treatments. In this article, we explore ‘Understanding Shockwave Tendonitis’ and delve into the scientific evidence supporting the efficacy of shockwave therapy. Furthermore, we present ‘Long-Term Relief’ success stories and research findings, offering hope for those struggling with this debilitating condition.”
- Understanding Shockwave Tendonitis: A Deep Dive
- Scientific Evidence for Shockwave Therapy Efficacy
- Long-Term Relief: Success Stories and Research Findings
Understanding Shockwave Tendonitis: A Deep Dive

Shockwave tendonitis is a condition characterized by inflammation and pain in tendons, often caused by repetitive stress or acute injuries. This condition can significantly impact mobility and daily activities, leading many to seek effective shockwave tendonitis relief. Understanding this disorder involves delving into its pathophysiology, where micro-tears in tendons trigger an inflammatory response, resulting in pain, swelling, and reduced function. The affected areas may include the Achilles tendon, patellar tendon, or tendons in the hands and feet.
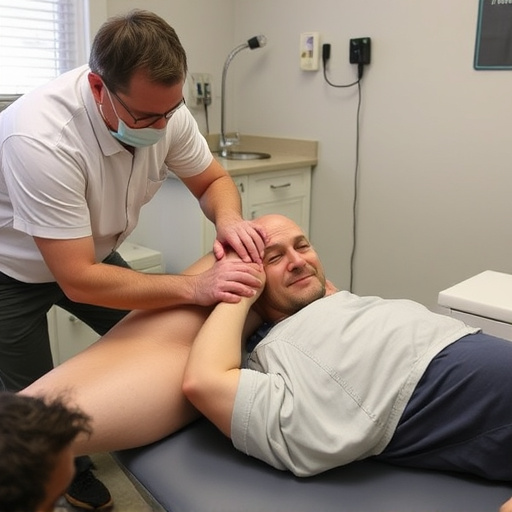
Post-injury care plays a pivotal role in managing shockwave tendonitis. Proper rest, physical therapy, and customized post accident rehabilitation programs can aid in healing and prevent further damage. Additionally, treatments like corticosteroid injections or surgical intervention might be considered for severe cases. However, with advancements in medical science, non-invasive methods like extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) have emerged as a game-changer in shockwave tendonitis relief. ESWT uses focused sound waves to stimulate healing and reduce pain, offering a promising alternative to conventional treatments, especially for those seeking back pain relief without invasive procedures.
Scientific Evidence for Shockwave Therapy Efficacy

The effectiveness of shockwave therapy for tendonitis has been backed by growing scientific evidence. Numerous studies have explored its potential in treating this common yet debilitating condition, with promising results. Research indicates that low-energy extracorporeal shockwaves (AES) can stimulate tissue repair and promote healing in affected tendons. This non-invasive approach has shown significant potential in relieving pain and improving function for individuals suffering from tendonitis.
Several clinical trials have demonstrated the efficacy of shockwave therapy in achieving shockwave tendonitis relief. These studies have found that AES can modulate inflammatory responses, enhance collagen synthesis, and improve overall tendon integrity. Moreover, it has been shown to facilitate injury rehabilitation and contribute to mobility improvement, making it a valuable addition to conventional treatment modalities for sciatica treatment and other related conditions.
Long-Term Relief: Success Stories and Research Findings

Many patients suffering from shockwave tendonitis find long-term relief through this innovative treatment method. Success stories abound, with individuals experiencing significant improvements in their quality of life after completing a series of shockwave therapy sessions. Research findings support these anecdotes, demonstrating that shockwave therapy can effectively reduce pain and promote tissue repair in tendinopathy cases.
A notable study compared the effectiveness of shockwave tendonitis relief to traditional treatments like corticosteroid injections. The results indicated that patients treated with shockwaves experienced greater pain reduction and improved functional capabilities over a prolonged period. Moreover, these positive outcomes were sustained even after the conclusion of therapy, suggesting that shockwave treatment offers durable results for managing this challenging condition. Personalized treatment plans tailored to individual needs play a crucial role in achieving optimal outcomes in whiplash treatment or sports injury recovery scenarios.
In conclusion, shockwave therapy has emerged as a highly effective treatment option for shockwave tendonitis, backed by robust scientific evidence. The successful long-term relief witnessed in numerous studies and patient stories underscores its potential to revolutionize the management of this painful condition. By non-invasively stimulating tissue repair, shockwaves offer a promising alternative to traditional treatments, providing patients with lasting comfort and improved mobility. For those seeking relief from shockwave tendonitis, exploring this innovative therapy could be a game-changer.